Forgejo Actions | Security of Pull Requests
A pull request may contain code that changes what is run by Forgejo
Actions, for instance if it modifies a file in the
.forgejo/workflows directory. When such a pull request originates
from a fork of a public repository on a Forgejo instance with open
registration, the author may be a malicious user. For this reason the
workflows of such pull requests need to be approved before they are run.
Users with elevated permissions on a repository can approve or deny workflows runs using the pull request conversation page.
Trust management
Trust is either granted or denied to the author of a pull request.
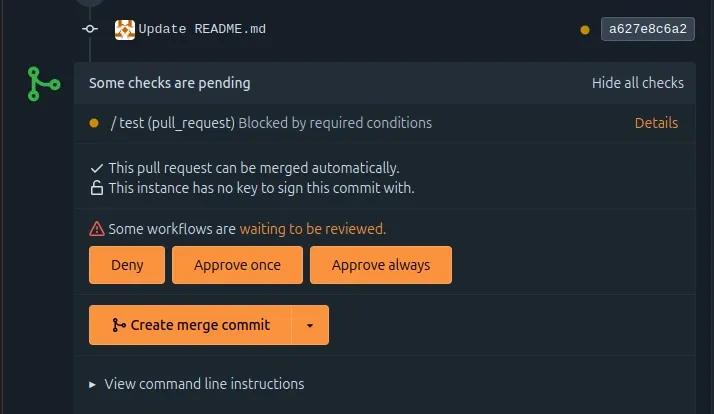
When using the Approve once button, all pending workflows will be
allowed to run. However future workflows will need another manual
approval (for instance if a new commit is pushed to the same pull request).
Using the Approve always button will trust the author of the pull request to always
run workflows on this repository.
It is possible to revoke that trust at any time.
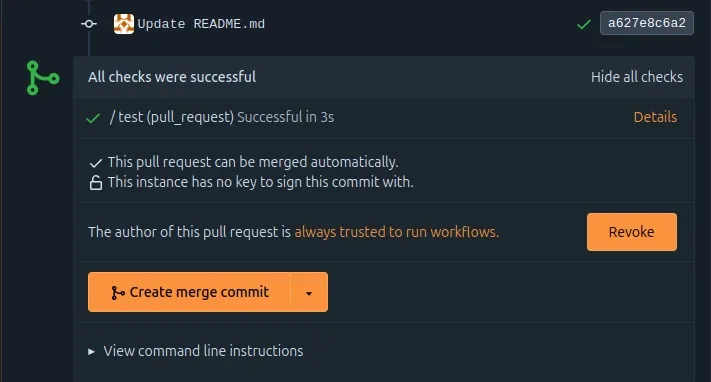
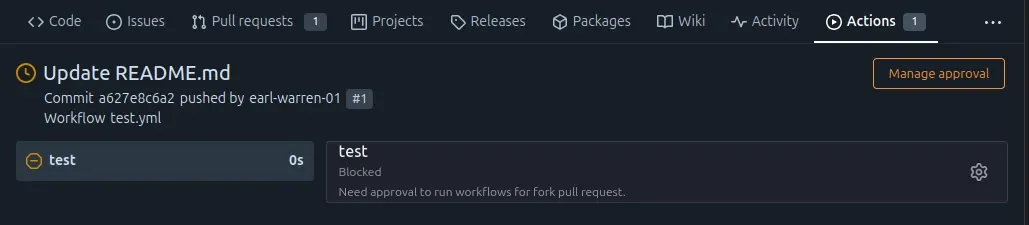
The page displaying the run of each blocked workflow shows a link to the trust management area of the pull request.
Which users need approval?
The users who only have read access to the repository need approval before workflows triggered by a pull request they authored can be run.
The users who have elevated permissions on the repository do not need approval, even if they author a pull request from a forked repository. That includes:
- Collaborators with write access
- Team members with write permissions on the
Actionsunit Ownersof the repository- Instance admins
The author of a pull request is held responsible for all commits they push to their pull request, including commits written by a third party. For instance, if a pull request is from a branch of a repository to which multiple users are allowed to push they are also implicitly trusted if the author of the pull request is trusted.
What pull requests need approval?
Assuming the author of a pull request is not implicitly trusted because of their elevated permissions, approval will be required for pull requests that are either:
- from a fork of the repository
- created using the
AGitworkflow
Which user can grant approval?
Trust management is available to users who are either:
- Collaborators with write access
- Team members with write permissions on the
Actionsunit Ownersof the repository- Instance admins
Which workflow files are used?
When a trusted user submits a pull request, workflows found in the
pull request content are used (except for the ones using the
pull_request_target event), taking into account any changes done to
these files as part of that pull request.
If the pull request is not from a trusted user and a workflow is triggered by a trusted user, the workflows found in the target branch of the pull request will be used instead of those found in the pull request.
A concrete use case is to allow the repository owner to set a label on a pull request from an untrusted user without having to verify if the pull request contains a malicious workflow.
Trust expiration
When a permanently trusted user has not submitted a pull request for over three months, the trust they may have been granted on a given repository will be automatically revoked.
Blocked users
When a user is blocked, the trust they were granted on all repositories owned by the user doing the blocking will be revoked.
All workflow runs created on their behalf on those repositories will be canceled.
